
BUTT-WELD FITTINGS
Used in large diameter, high-pressure pipelines. Welded directly to pipes for permanent installations.
FittingDescription
Elbow (45°, 90°, 180°)
Changes direction of flow. 45° for slight turns, 90° for right-angle turns, and 180° for return flow.
Tee (Equal / Reducing)
Creates a 90° branch. Equal tee connects same-size pipes; reducing tee connects pipes of different diameters.
Reducer (Concentric / Eccentric)
Concentric: used for vertical lines; symmetrical. Eccentric: used for horizontal lines to prevent air pockets.
End Cap
Closes the end of a pipe, preventing flow.
Stub End
Used with lap joint flanges for easy disassembly in flanged connections.
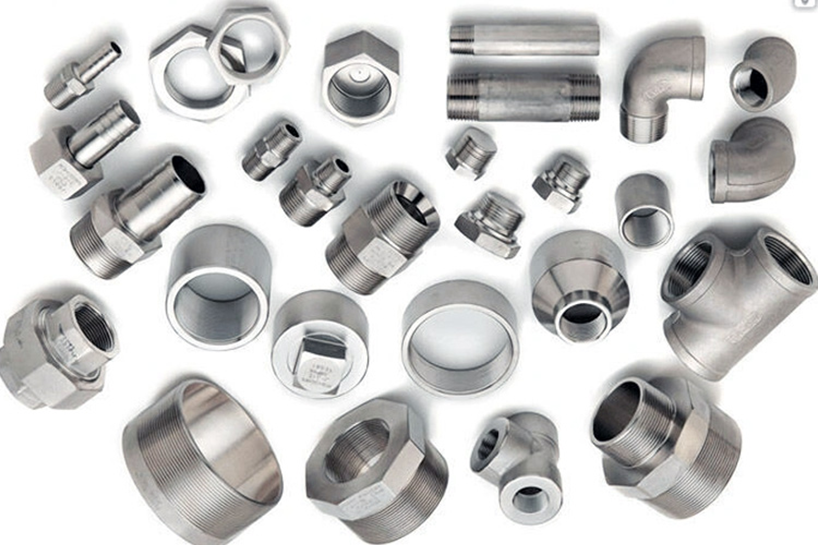

Elbow (Threaded / Socket Weld) Turns the flow direction in the pipeline (usually 90° or 45°).
Tee (Threaded / Socket Weld) Divides flow into two branches or joins three flows.
Coupling (Full / Half) Connects two pipes together; half coupling connects pipe to equipment or valve.
Union Allows quick and easy disconnection of pipe segments.
Plug Closes the pipe end temporarily or permanently.
Cap Similar to plug but covers the outside diameter of the pipe.
Bushing Connects pipes of different diameters with internal and external threads.
Cross Four-way fitting that splits flow into three branches at 90° angles.
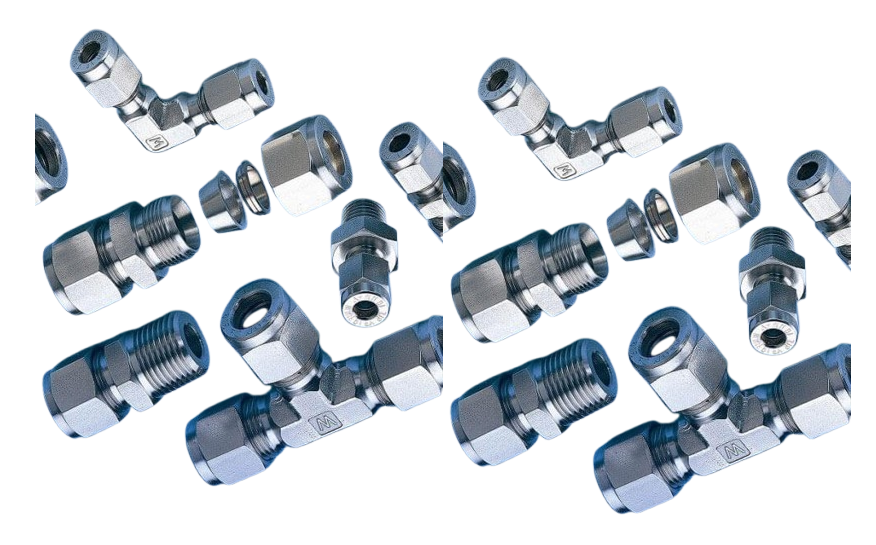

Male / Female Connector Connects tubing to male/female threads respectively.
Bulkhead Union Passes tubing through panels or walls while maintaining a sealed connection.
Union (Straight / Elbow / Tee) Joins two or more tubes inline (straight), at 90° (elbow), or branches flow (tee).
Reducer Connects tubes of different sizes while maintaining leak-proof connection.
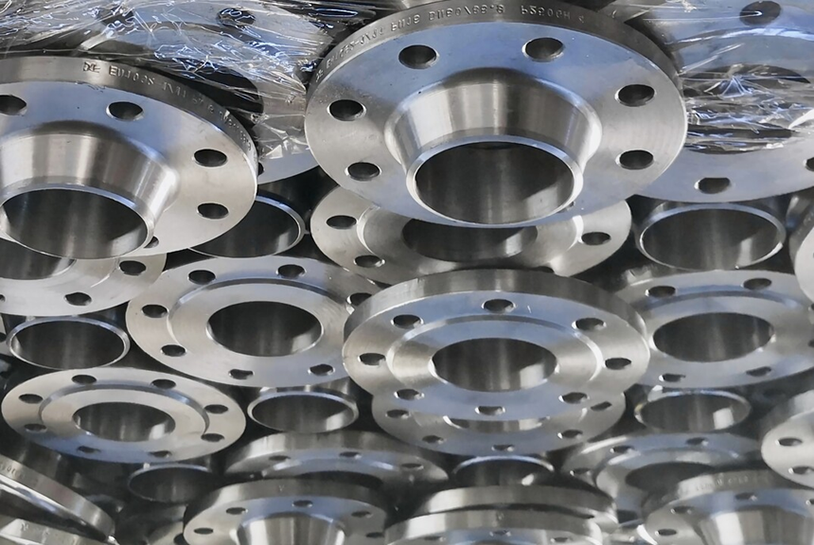

Slip-On Flange Slips over the pipe; easy to install and weld.
Weld Neck Flange High strength, used in high-pressure and high-temperature systems.
Blind Flange Closes the end of a piping system.
Socket Weld Flange For small-size, high-pressure systems; pipe is inserted into socket.
Threaded Flange Screws onto threaded pipe without welding; used in low-pressure systems.
Lap Joint Flange Used with stub ends; allows rotation for bolt alignment.
Orifice Flange For flow measurement in pipelines using an orifice meter.
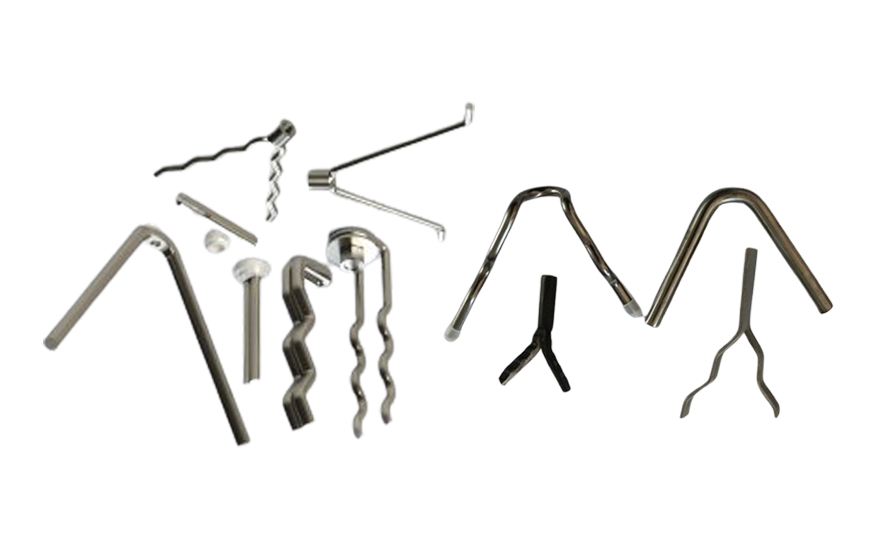

🔩 What Are Refractory Anchors? Refractory anchors are metal fixing or fastening components embedded into refractory linings to securely tie the refractory to the kiln shell or support structure. They:
V-Type
Standard castable anchoring; simple & cost-effective
Y-Type
Better pull-out resistance; deeper support for thicker lining
U-Type
Handles differential expansion; good in modular/precast linings
Zig-Zag / Corrugated
Larger surface contact; excellent mechanical interlock
Straight / Stud
Simple pin anchors for castable & bricks
Custom
Tailored for special geometry & service conditions

304 – General-purpose grade with good corrosion resistance and formability.
304L – Low carbon version of 304 for better weldability.
316 – Enhanced corrosion resistance with molybdenum, ideal for marine and chemical use.
316L – Low carbon version of 316 for excellent weldability and corrosion resistance.
310 – High-temperature resistant; used in heat and oxidation-prone environments.
310S – Lower carbon variant of 310 for better weldability in high-temperature applications.
321 – Stabilized with titanium; resists intergranular corrosion during welding.
347 – Stabilized with niobium; suitable for high-temp, high-stress environments.
347H – High carbon version of 347 for better strength at elevated temperatures.
904L – Super austenitic steel with excellent resistance to aggressive acids.
317 – Higher molybdenum content than 316 for added corrosion protection.
317L – Low carbon version of 317 for better weldability.
Duplex 2205 – High strength and resistance to pitting and stress corrosion.
Super Duplex 2507 – Superior strength and corrosion resistance for harsh environments.
410 – Martensitic steel with good strength and moderate corrosion resistance.
430 – Ferritic stainless with good oxidation and corrosion resistance; non-hardenable.

ASTM A234 WPB – Most commonly used grade for butt-weld fittings; suitable for moderate to high temperature and pressure applications.
ASTM A105 – Forged carbon steel used for flanges, socket weld, and threaded fittings in highpressure systems.
ASTM A106 Gr. B – Seamless carbon steel pipe grade, often used for high-temp service; fittings match for pressure pipelines.
ASTM A420 WPL6 – Low-temperature carbon steel used in cryogenic and cold service piping systems.
ASTM A694 F42 / F46 / F52 / F60 / F65 / F70 – High-strength forged fittings and flanges used in highpressure transmission service (mostly oil & gas pipelines).
IS 1239 / IS 3589 – Indian Standards for mild steel pipe fittings used in low-pressure and water distribution systems.
ASTM A860 WPHY 42 / 46 / 52 / 60 / 65 / 70 – High-yield strength wrought fittings for use in gas, oil, and high-pressure services.

ASTM A234 WP1 – Low alloy steel for moderate temperature service, commonly used in power plants.
ASTM A234 WP5 – Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel, ideal for high-temp environments like refineries and boilers.
ASTM A234 WP9 – High-performance alloy with good strength and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures.
ASTM A234 WP11 – Widely used in high-temperature and pressure systems like petrochemical plants.
ASTM A234 WP22 – Excellent for high-pressure steam and power generation service.
ASTM A234 WP91 – Advanced creep-resistant alloy for ultra high-temperature and pressure environments.
ASTM A182 F5 / F9 / F11 / F22 / F91 – Forged alloy grades used in flanges and fittings for hightemp, high-stress applications.
ASTM A335 P1 / P5 / P9 / P11 / P22 / P91 – Seamless alloy steel pipe grades; fittings are often matched accordingly.

Stainless Steel Tube, Stainless Steel Pipe
📐 Product Size
Outer Diameter: 6 mm – 2000 mm
Thickness: 0.1 mm – 100 mm (Customizable)
Length: ≤ 12000 mm or as per customer requirement
� Standards ASTM A213, ASTM A312, ASTM A789, ASTM A790, etc.
🧪 Grades
201, 202, 304, 304L, 304H, 316, 316L, 316Ti, 2205, 330, 630, 660, 409L, 321, 310, 410, 416, 410S, 430, 347H, 2Cr13, 3Cr13
300 Series
301, 302, 303, 304, 304L, 309, 309S, 310, 310S, 316, 316L, 316Ti, 317L, 321, 347
200 Series
201, 202, 202Cu, 204
400 Series
409, 409L, 410, 420, 430, 431, 439, 440, 441, 444
Duplex Stainless Steel
S22053, S25073, S22253, S31803, S32205, S32304
Special Stainless Steel
904L, 347/347H, 317/317L, 316Ti, 254Mo
Others
2205, 2507, 2906, 330, 660, 630, 631, 17-4PH, 17-7PH, S31803, 904L
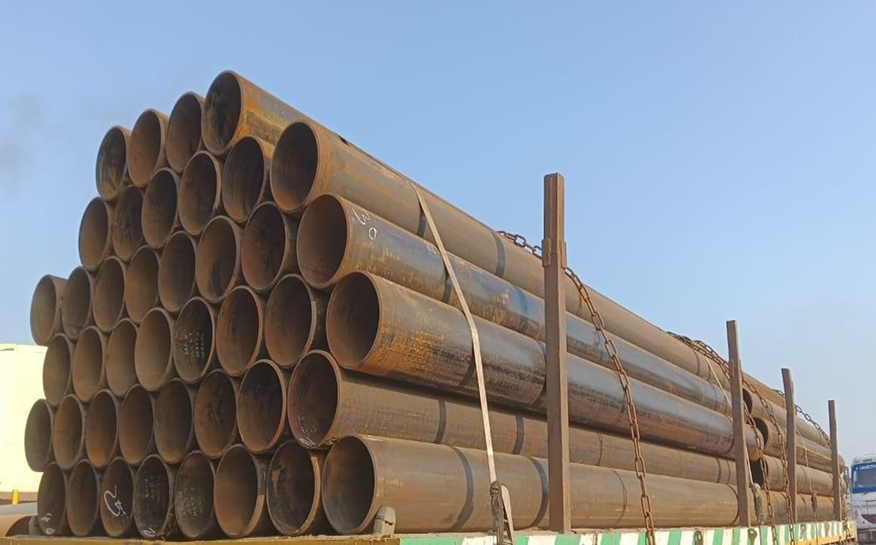

📏 Standards ASTM A53, ASTM A106, API 5L, ASTM A333, ASTM A210, ASTM A179, ASTM A252, etc.
🧪 Grades Seamless Pipe Grades ASTM A106 Gr. A / B / C ASTM A53 Gr. A / B API 5L Gr. B / X42 / X46 / X52 / X60 / X65 / X70 ASTM A333 Gr. 1 / 3 / 6 (Low Temp) ASTM A179, A210 (Boiler & Heat Exchanger Tubes) Welded Pipe Grades ASTM A53 Gr. A / B ASTM A252 Gr. 1 / 2 / 3 (Piling Pipes) API 5L Gr. B to X70 (ERW / LSAW / SSAW)
📐 Product Size Outer Diameter: 6 mm – 2000 mm Thickness: 0.5 mm – 100 mm (Customizable) Length: ≤ 12000 mm or as per customer requirement
🧰 End Types Plain End (PE) Beveled End (BE) Threaded End (TE)
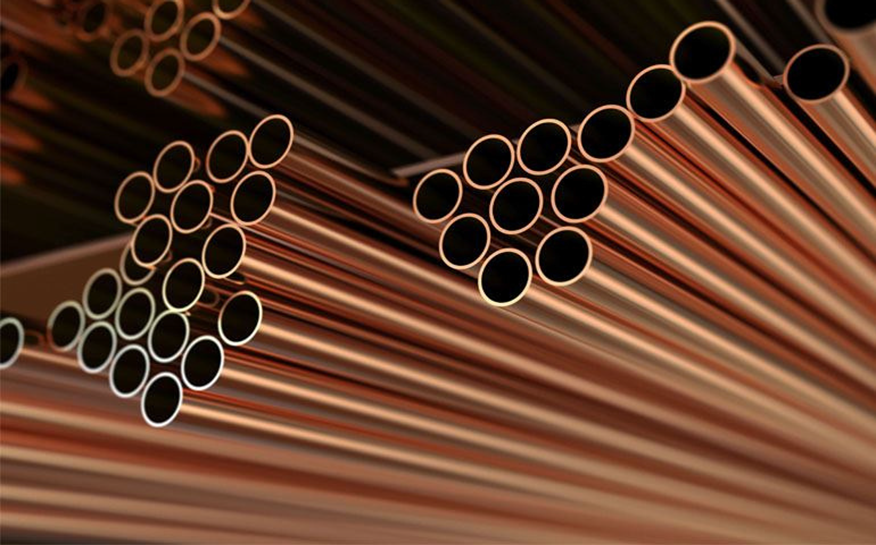

Pure Copper Grades
C10100 – Oxygen-Free Electronic (OFE) Copper
C10200 – Oxygen-Free (OF) Copper
C10300 – Oxygen-Free, Extra Low Phosphorus
C10400 – Oxygen-Free, Low Phosphorus
C10500 – Oxygen-Free, High Phosphorus
C10700 – Oxygen-Free, Extra High Phosphorus
C11000 – Electrolytic Tough Pitch (ETP) Copper
C11300 – Tough Pitch, Arsenical Copper
C12000 – Deoxidized Low Phosphorus (DLP) Copper
C12200 – Deoxidized High Phosphorus (DHP) Copper